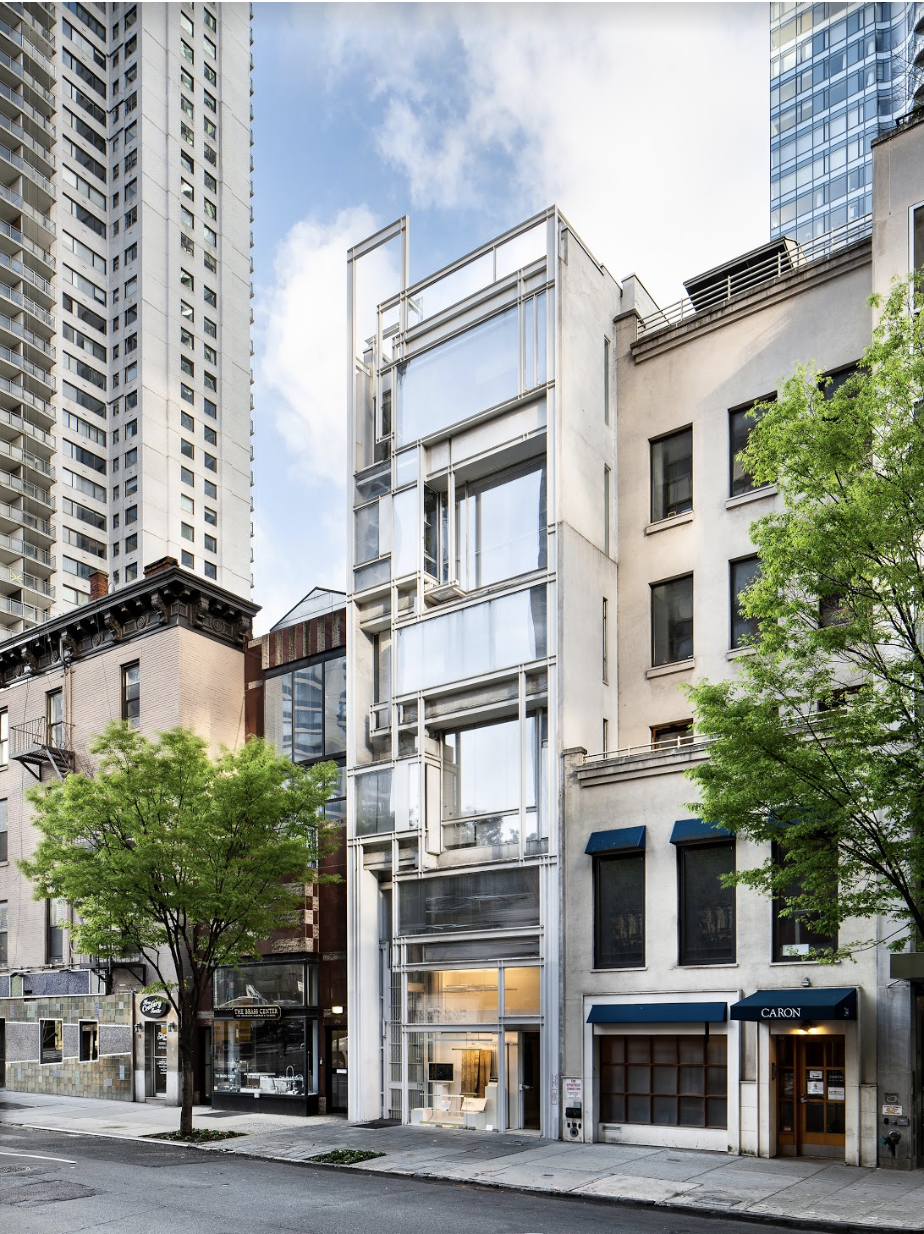
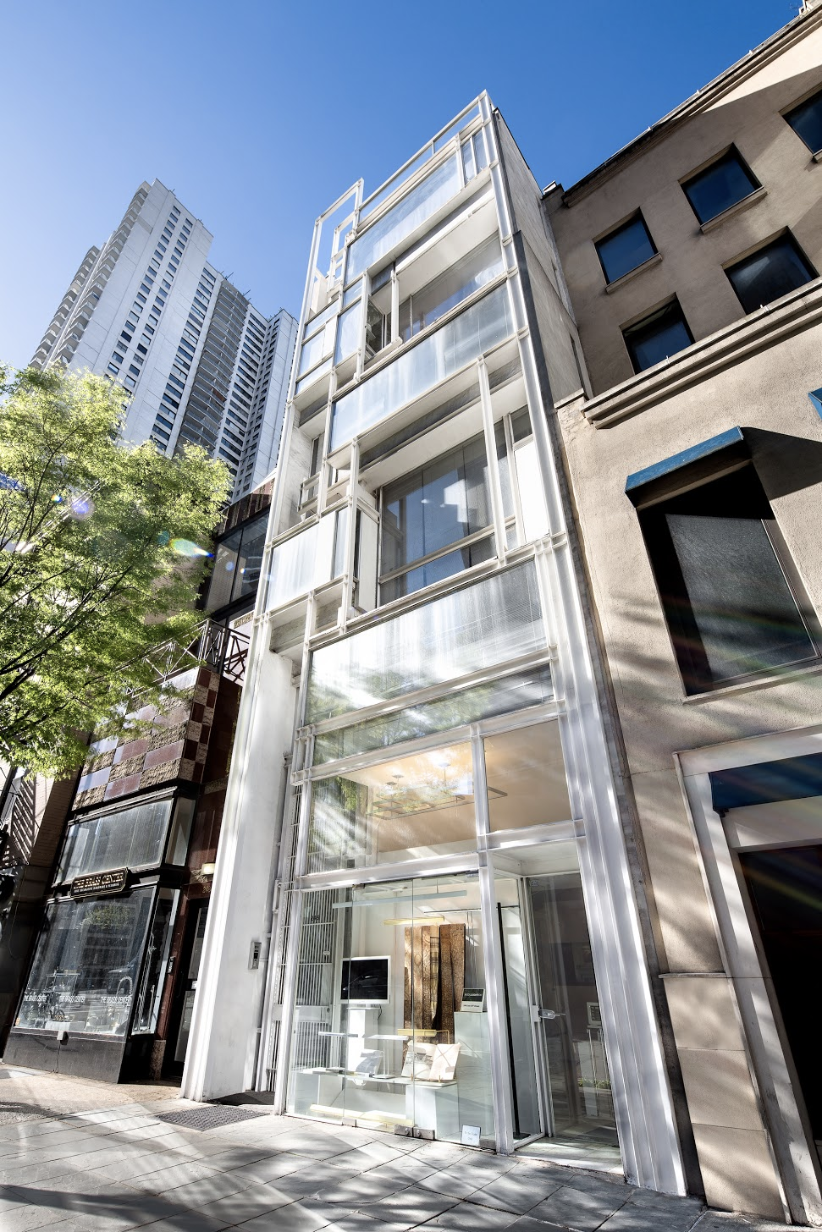
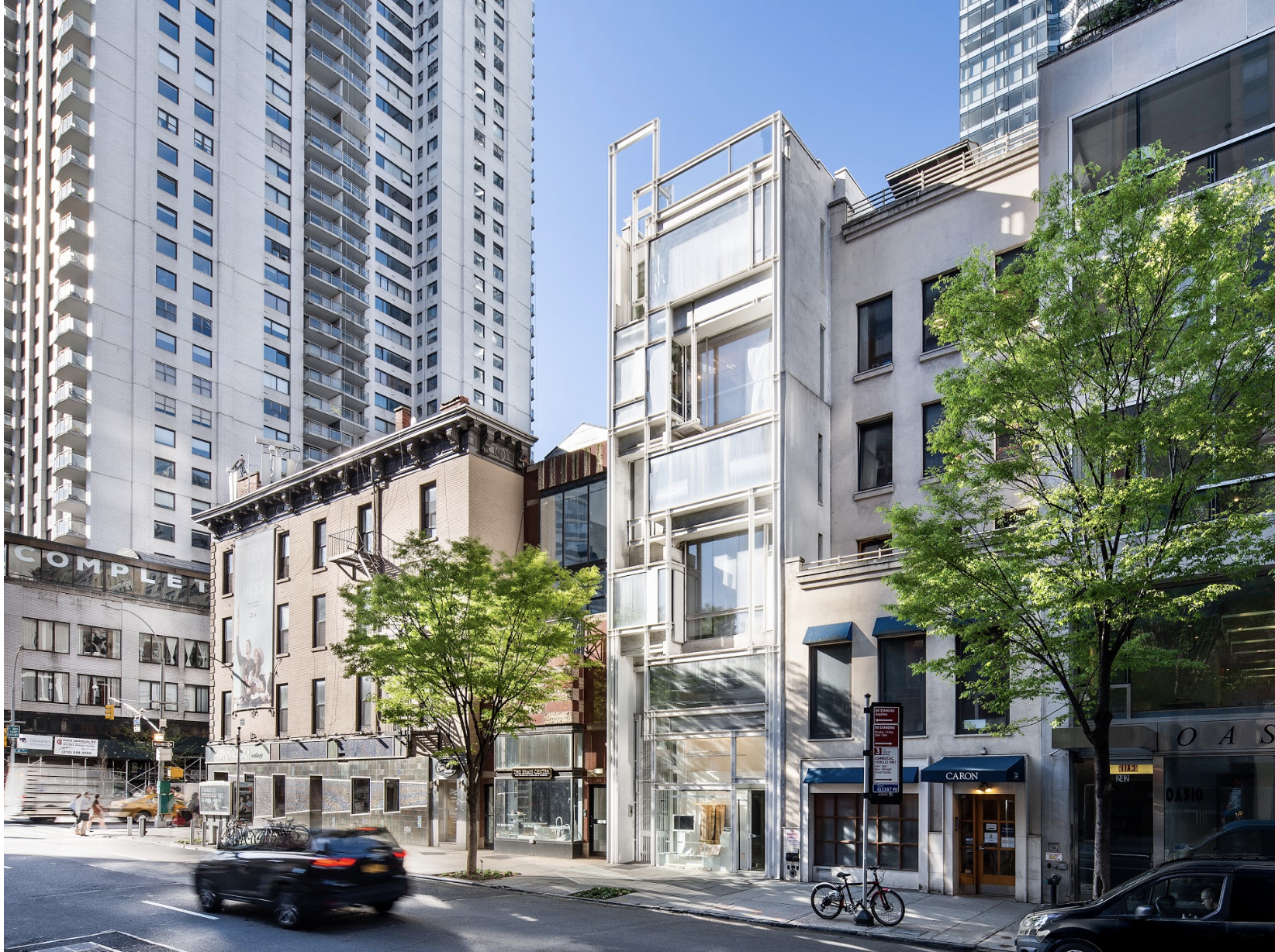
Paul Rudolph’s original rendering of the front of the Modulightor showroom in the Modulightor building
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
The Paul Rudolph Institute For Modern Architecture
01/17/2025
The Modulightor Lighting Company Is gifted to the Paul Rudolph Institute, Announces New Directors
New Directors Continue Paul Rudolph’s Vision to create Situation-specific Custom Lighting Using his Original Designs
NEW YORK, NY (January 17, 2025) –The Paul Rudolph Institute for Modern Architecture (“PRIMA”) announced it was gifted the Modulightor Lighting Company following the death of its owner, Ernst Wagner, this past December. The Modulightor building, the company’s headquarters, was gifted to the Institute in 2023 while Mr. Wagner was still living.
Ever since it was founded in 1976 by legendary Modernist architect Paul Rudolph, the Modulightor lighting company has been at the center of lighting technology and design across New York City and the world.
The Board of the Institute announced the appointment of current board members Kelvin Dickinson and Santo Pusateri as Directors of Modulightor, along with Julian Aleksandres, who was Modulightor’s showroom manager from 2005 until 2014.
Kelvin Dickinson
Santo Pusateri
Julien Aleksandres
“The Paul Rudolph Institute educates the public about Mr. Rudolph’s interest in lighting and modularity using the fixtures he designed for Modulightor as real world examples,” said Kelvin Dickinson, President of PRIMA. “We worked closely with Ernst, who also founded the Paul Rudolph Institute, on this effort. We’re grateful to have the opportunity to show that Rudolph’s original vision continues to inspire architects and designers.”
About the Modulightor Lighting Company
Paul Rudolph saw a need for situation-specific lighting — something that was not addressed by the lighting industry available at the time — and his insights led the way to creating lighting solutions that continue to be unique in the industry. The conceptual framework for Modulightor was informed by Le Corbusier’s landmark 1950 book, Le Modulor, which proposed a sequence of measurements to achieve architectural harmony. Over the years, Rudolph and Wagner translated and engineered Le Corbusier’s ideas on modularity into an erector-set-like concept for lighting.
With Rudolph lending a guiding hand, Wagner developed a system of modular parts that can be combined into a seemingly endless array of fixtures. Modulightor’s standard parts, luminaires and bulbs can be joined and grouped so that the form, function, proportions, dimensions and finishes of each light perfectly satisfy the designer’s vision and client’s needs.
For nearly 50 years, Modulightor’s modular, scalable, and adaptable lighting systems — all based on Rudolph’s original designs and observations on light and its relationship to space, form and surface – have been available in a range of extrusion-based fixtures.
All of the lighting designed by Modulightor is manufactured onsite in the landmark Modulightor Building in New York City, making it one of the last lighting companies left in the city to still do so.
For more information about the Modulightor lighting company, visit www.modulightor.com and find them as @modulightor on Facebook and Instagram.
About the Paul Rudolph Institute for Modern Architecture
The Paul Rudolph Institute for Modern Architecture is a New York City-based non-profit 501(c)3 organization dedicated to educating the public about modern architecture and the need to preserve it. Through preservation and advocacy efforts, educational programs, public events and maintaining and developing an archive of written and graphic materials, the Institute promotes the legacy of modernist architects in a larger architectural and cultural context to interested students, journalists, scholars, and the general public.
For more information about the Paul Rudolph Institute for Modern Architecture, visit www.paulrudolph.institute and find them as @PaulRudolphInst on Bluesky, Threads, Twitter, Facebook and Instagram.
Media Contact:
Santo Pusateri
office@paulrudolph.institute
(212) 404-5922
www.paulrudolph.institute
Download the press release here.